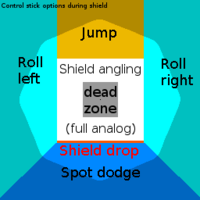
Shield drop
Shield platform dropping, commonly called shield dropping, is an advanced technique in all Super Smash Bros. games up until Super Smash Bros. 4. It involves dropping through a soft platform while shielding by tilting the analog stick down.
The term "shield drop" should not be confused with "dropping one's shield", which refers to when one lets go of the shield button and stops shielding.
In Super Smash Bros.
The technique is simple to execute in Smash 64, as there is no sidestepping in that game to interfere with the function of pressing the stick downward while shielding.
In Super Smash Bros. Melee
As the sidestep is introduced in Melee, pressing the control stick too far and too fast results in a sidestep. Since this makes it hard to platform drop while shielding, the player must either be very precise with their inputs or press the stick down during a different action than shielding (such as a dash or shield stun) with close enough timing that the sidestep window is closed but the drop window is still open.
This "window" is made considerably easier to hit using the Axe/Sung method, wherein you fully angle shield left or right(after doing an aerial/waveland onto a platform, or by slowly tilting it manually), then rotate the stick downward to the next notch(From full left to down-left, or full right to down-right.) Because of the alignment of the diagonal notch being generally close to this range of values, this can allow you to quickly buffer shield drops with one control stick input out of shield stun without accidentally spot dodging.(which is what you will often see if people mess up their shield drops.) Because the margin of error for getting a successful shield drop is limited to ONLY three Y axis values, Shield dropping is frequently very controller dependent. Many modern official gamecube controllers are able to do it to the left out of the box but not the right.
While this would normally be a huge issue, many melee players modify their controllers temporarily and permanently to have a control stick gate that aligns with these values on both sides. These are called "shield drop notches" and are generally pretty simple to do with modern tools. If not, there are many controller modders around who are able to do this for you, and it can be relatively cheap. The alternative temporary solution is to use tape on your control stick gate, to "pad" the corner enough that your stick hits the necessary values.
In Super Smash Bros. Brawl

In Brawl, while the conflict between sidestepping and dropping persists, there is now a small window where a drop can be made without triggering a sidestep: the player must move the control stick down to 68.75% of its maximum downwards angle in 6 frames without moving it past 70% of said angle in 4 frames.
In Super Smash Bros. 4
In SSB4, the technique remains the same as in Brawl. However, it is possible to perform a down smash or grounded down special immediately out of shield on a platform if the control stick is moved down just slightly less than that of the regular shield drop angle. Additionally, and perhaps most interestingly, Yoshi loses the ability to shield drop and perform the previously mentioned technique due to his unique shield.
Uses
The primary use of shield dropping is to punish the use of moves on a shielding player on a platform, as it allows players to quickly do an aerial out of shield to punish ending lag. Shield platform dropping opens a larger possibility of comboing, tech-chasing, edgeguarding, mindgaming, and out-of-shield options. The player can run and pass under the platform, which cannot be done without shielding in Brawl. This technique also gives Yoshi a quick way to act out of his unique shield, as he cannot jump out of shield in Melee and Brawl.